Way to Glow
On-Site School Program
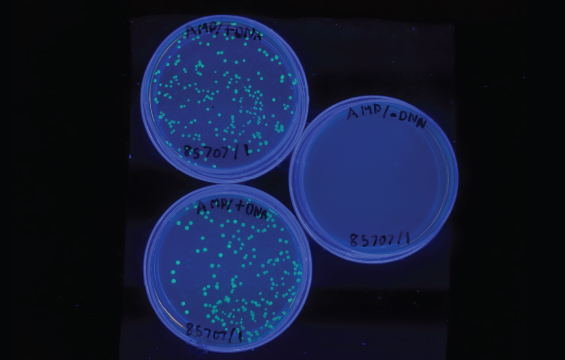
Curriculum Connections:
Strands A, B and D : Scientific Investigation Skills, Diversity of Living things & Genetic Processes
| A1.1 | formulate relevant scientific questions about observed relationships, ideas, problems, or issues, make informed predictions, and/or formulate educated hypotheses to focus inquiries or research |
|---|---|
| A1.4 | apply knowledge and understanding of safe laboratory practices and procedures when planning investigations by correctly interpreting Workplace Hazardous Materials Information System (WHMIS) symbols; by using appropriate techniques for handling and storing laboratory equipment and materials and disposing of laboratory and biological materials (e.g., preserved specimens); and by using appropriate personal protection |
| A1.5 | conduct inquiries, controlling relevant variables, adapting or extending procedures as required, and using appropriate materials and equipment safely, accurately, and effectively, to collect observations and data |
| A1.8 | synthesize, analyse, interpret, and evaluate qualitative and/or quantitative data to determine whether the evidence supports or refutes the initial prediction or hypothesis and whether it is consistent with scientific theory; identify sources of bias and/or error; and suggest improvements to the inquiry to reduce the likelihood of error |
| A1.10 | draw conclusions based on inquiry results and research findings, and justify their conclusions with reference to scientific knowledge |
| B3.2 | compare and contrast the structure and function of different types of prokaryotes, eukaryotes, and viruses (e.g., compare and contrast genetic material, metabolism, organelles, and other cell parts) |
| B3.3 | describe unifying and distinguishing anatomical and physiological characteristics (e.g., types of reproduction, habitat, general physical structure) of representative organisms from each of the kingdoms |
| B3.5 | explain why biodiversity is important to maintaining viable ecosystems (e.g., biodiversity helps increase resilience to stress and resistance to diseases or invading species) |
| D1.2 | evaluate, on the basis of research, the importance of some recent contributions to knowledge, techniques, and technologies related to genetic processes |
| D2.1 | use appropriate terminology related to genetic processes, including, but not limited to: haploid, diploid, spindle, synapsis, gamete, zygote, heterozygous, homozygous, allele, plasmid, trisomy, non-disjunction, and somatic cell |
| D3.3 | explain the concepts of genotype, phenotype, dominance, incomplete dominance, codominance, recessiveness, and sex linkage according to Mendelian laws of inheritance |
Strands A, C and D : Scientific Investigation Skills, Microbiology & Genetics
| A1.1 | formulate relevant scientific questions about observed relationships, ideas, problems, or issues, make informed predictions, and/or formulate educated hypotheses to focus inquiries or research |
|---|---|
| A1.4 | apply knowledge and understanding of safe laboratory practices and procedures when planning investigations by correctly interpreting Workplace Hazardous Materials Information System (WHMIS) symbols; by using appropriate techniques for handling and storing laboratory equipment and materials and disposing of laboratory and biological materials (e.g., preserved specimens); and by using appropriate personal protection |
| A1.5 | conduct inquiries, controlling relevant variables, adapting or extending procedures as required, and using appropriate materials and equipment safely, accurately, and effectively, to collect observations and data |
| A1.8 | synthesize, analyse, interpret, and evaluate qualitative and/or quantitative data to determine whether the evidence supports or refutes the initial prediction or hypothesis and whether it is consistent with scientific theory; identify sources of bias and/or error; and suggest improvements to the inquiry to reduce the likelihood of error |
| A1.10 | draw conclusions based on inquiry results and research findings, and justify their conclusions with reference to scientific knowledge |
| C2.1 | use appropriate terminology related to microbiology, including, but not limited to: fission, conjugation, phage, dormancy, morphology, mycelium, spore, pathogen, and plasmid |
| C2.3 | prepare a laboratory culture of microorganisms (e.g., acidophilus) on agar, using proper aseptic techniques |
| C2.4 | investigate the effect of antibacterial agents on different bacterial cultures (e.g., the effects of antibacterial soap or mouthwash on a bacterial culture) |
| D3.2 | explain how the concepts of DNA, genes, chromosomes, alleles, mitosis, and meiosis account for the transmission of hereditary characteristics from generation to generation |
| D3.3 | explain the concepts of genotype, phenotype, dominance, recessiveness, and sex linkage |
Strands A, B and D : Scientific Investigation Skills, Biochemistry and Molecular Genetics
| A1.1 | formulate relevant scientific questions about observed relationships, ideas, problems, or issues, make informed predictions, and/or formulate educated hypotheses to focus inquiries or research |
|---|---|
| A1.4 | apply knowledge and understanding of safe laboratory practices and procedures when planning investigations by correctly interpreting Workplace Hazardous Materials Information System (WHMIS) symbols; by using appropriate techniques for handling and storing laboratory equipment and materials and disposing of laboratory and biological materials (e.g., preserved specimens); and by using appropriate personal protection |
| A1.5 | conduct inquiries, controlling relevant variables, adapting or extending procedures as required, and using appropriate materials and equipment safely, accurately, and effectively, to collect observations and data |
| A1.8 | synthesize, analyse, interpret, and evaluate qualitative and/or quantitative data to determine whether the evidence supports or refutes the initial prediction or hypothesis and whether it is consistent with scientific theory; identify sources of bias and/or error; and suggest improvements to the inquiry to reduce the likelihood of error |
| A1.10 | draw conclusions based on inquiry results and research findings, and justify their conclusions with reference to scientific knowledge |
| B1.2 | evaluate, on the basis of research, some advances in cellular biology and related technological applications |
| B2.2 | plan and conduct an investigation to demonstrate the movement of substances across a membrane |
| B2.5 | plan and conduct an investigation related to a cellular process using appropriate laboratory equipment and techniques, and report the results in an appropriate format |
| B3.2 | describe the structure of important biochemical compounds, including carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids, and explain their function within cells |
| B3.6 | describe the structure of cell membranes according to the fluid mosaic model, and explain the dynamics of passive transport, facilitated diffusion, and the movement of large particles across the cell membrane by the processes of endocytosis and exocytosis |
| D3.5 | describe some examples of genetic modification, and explain how it is applied in industry and agriculture |
| D3.6 | describe the functions of some of the cell components used in biotechnology |
| D3.7 | describe, on the basis of research, some of the historical scientific contributions that have advanced our understanding of molecular genetics |
Strands A and F : Scientific Investigation Skills and Biotechnology
| A1.1 | formulate relevant scientific questions about observed relationships, ideas, problems, or issues, make informed predictions, and/or formulate educated hypotheses to focus inquiries or research |
|---|---|
| A1.4 | apply knowledge and understanding of safe laboratory practices and procedures when planning investigations by correctly interpreting Workplace Hazardous Materials Information System (WHMIS) symbols; by using appropriate techniques for handling and storing laboratory equipment and materials and disposing of laboratory and biological materials (e.g., preserved specimens); and by using appropriate personal protection |
| A1.5 | conduct inquiries, controlling relevant variables, adapting or extending procedures as required, and using appropriate materials and equipment safely, accurately, and effectively, to collect observations and data |
| A1.8 | synthesize, analyse, interpret, and evaluate qualitative and/or quantitative data to determine whether the evidence supports or refutes the initial prediction or hypothesis and whether it is consistent with scientific theory; identify sources of bias and/or error; and suggest improvements to the inquiry to reduce the likelihood of error |
| A1.10 | draw conclusions based on inquiry results and research findings, and justify their conclusions with reference to scientific knowledge |
| F1.1 | analyse social issues related to an application of biotechnology in the health, agricultural, or environmental sector |
| F2.1 | use appropriate terminology related to biotechnology, including, but not limited to: selective breeding, hybridization, replication, mutation, genomics, and gene therapy |
| F2.3 | investigate, through laboratory inquiry or computer simulation, a recently developed biotechnological method used in the health sector |
| F3.1 | explain various methods used, over time, in the field of biotechnology |
| F3.3 | describe applications of biotechnology in the health, agricultural and environmental sectors |
Strands A and D : Scientific Investigation Skills and Disease and its Prevention
| A1.1 | formulate relevant scientific questions about observed relationships, ideas, problems, or issues, make informed predictions, and/or formulate educated hypotheses to focus inquiries or research |
|---|---|
| A1.4 | apply knowledge and understanding of safe laboratory practices and procedures when planning investigations by correctly interpreting Workplace Hazardous Materials Information System (WHMIS) symbols; by using appropriate techniques for handling and storing laboratory equipment and materials and disposing of laboratory and biological materials (e.g., preserved specimens); and by using appropriate personal protection |
| A1.5 | conduct inquiries, controlling relevant variables, adapting or extending procedures as required, and using appropriate materials and equipment safely, accurately, and effectively, to collect observations and data |
| A1.8 | synthesize, analyse, interpret, and evaluate qualitative and/or quantitative data to determine whether the evidence supports or refutes the initial prediction or hypothesis and whether it is consistent with scientific theory; identify sources of bias and/or error; and suggest improvements to the inquiry to reduce the likelihood of error |
| A1.10 | draw conclusions based on inquiry results and research findings, and justify their conclusions with reference to scientific knowledge |
| D2.2 | conduct an investigation, using safe practices and aseptic techniques, to compare the characteristics and growth of different types of non-pathogenic bacteria |
| D2.3 | investigate the effects of various drug therapies on the growth of bacteria |


